Watch the Video Tutorial
💡 Pro Tip: After watching the video, continue reading below for detailed step-by-step instructions, code examples, and additional tips that will help you implement this successfully.
Hey there, future automation wizard! Boyce here, and if you’re anything like me, you’ve probably dabbled with AI agents in n8n and thought, “This is cool, but what if I could really make it sing?” Well, you’re in luck! Today, we’re diving deep into one of n8n’s best-kept secrets: the LangChain Code Node. This little gem is your golden ticket to building AI agents that are not just smart, but truly customized to your wildest automation dreams. Think of it like building LEGOs, but instead of following the instructions, you’re designing the entire spaceship from scratch!
I’ve spent countless hours wrestling with different platforms and frameworks, trying to get AI to do exactly what I want. And let me tell you, the frustration is real! But through all that, I’ve found that the LangChain Code Node in n8n is a game-changer. It gives you the kind of granular control that most pre-packaged solutions can only dream of. So, if you’re ready to stop being a passenger and start being the pilot of your AI agents, buckle up! We’re about to unlock some serious power.
Table of Contents
Open Table of Contents
- The Power of the LangChain Code Node in n8n
- What is LangChain?
- LangChain vs. OpenAI Assistants API: A Comparative Analysis
- Advanced Monitoring with LangSmith
- Building Customizable AI Agents with LangChain Code Node
- Critical Safety / Best Practice Tips
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Why should I use the LangChain Code Node instead of the standard AI Agent node?
- Q: Is the LangChain Code Node difficult to use for beginners?
- Q: Can I use different LLMs (like Claude and GPT) within a single LangChain Code Node workflow?
- Q: What are “tools” in the context of LangChain agents, and why are they important?
- Q: How does LangSmith help with my n8n AI agents?
The Power of the LangChain Code Node in n8n
Alright, let’s get down to business. Most of us n8n users are pretty familiar with the standard AI Agent node. It’s super handy for quickly getting an AI agent up and running, right? It abstracts away a lot of the complexity, which is great for quick wins. But what if you need to go beyond the basics? What if you need to tell your AI agent, “Hey, don’t just answer, but also check this database, then send an email, and then answer, but only if the database says X”?
That’s where the LangChain Code Node comes in. It’s like the engine room of the AI Agent node. While the AI Agent node is the shiny dashboard, the LangChain Code Node is where you get to tinker with the actual gears and levers. It offers a level of control that lets you truly fine-tune your AI agent’s behavior.
Discovering the LangChain Code Node
Now, here’s a little secret: the LangChain Code Node isn’t exactly front and center. It’s a bit like a hidden Easter egg in n8n. You won’t find it by just typing “LangChain” into the node search bar. Nope, you’ve got to go on a little treasure hunt!
To find it, you’ll need to:
- Click the
+button to add a new node. - Search for
AI. - Then, look for
Other AI nodes. - And finally, under that, you’ll see
Miscellaneous.
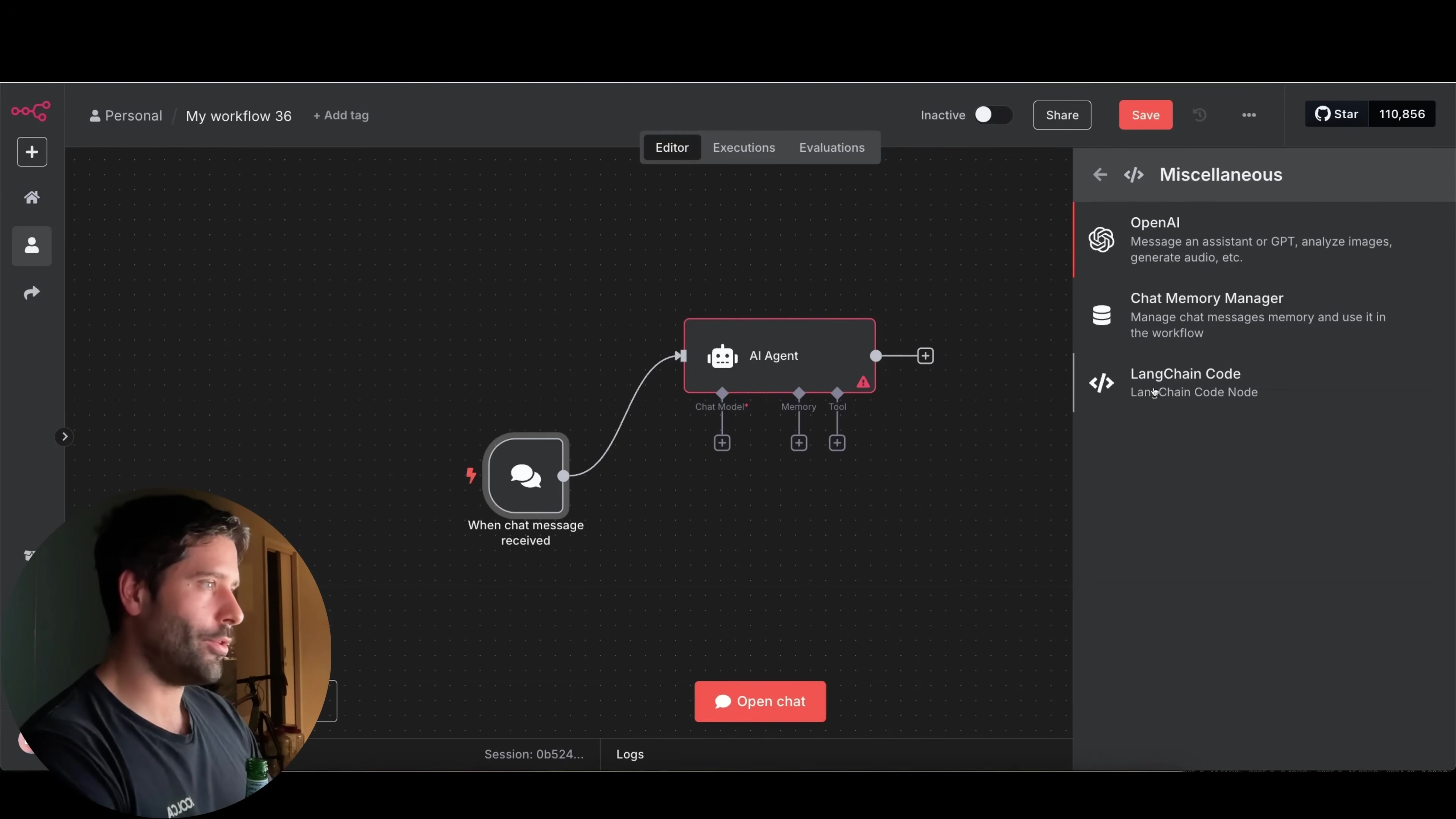
See? It’s tucked away! This unassuming node, which might look a bit blank at first glance (no immediate inputs or outputs, what gives?!), is actually the key to unlocking some seriously advanced customization. Don’t let its humble appearance fool you; it’s a powerhouse in disguise!
Unveiling the Underlying Mechanism
Here’s a mind-blowing fact: those convenient, high-level LLM nodes you love in n8n – like the Basic LLM Chain, Information Extractor, Question and Answer, and Text Summarization – are all built on top of the LangChain Code Node! Mind blown, right? This means that by learning to use the LangChain Code Node directly, you’re essentially getting access to the foundational building blocks that power all those other fancy AI steps.
Think of it this way: the other nodes are like pre-built houses, but the LangChain Code Node gives you the raw materials (bricks, wood, cement) and the blueprints to build any house you can imagine. Pretty cool, huh?
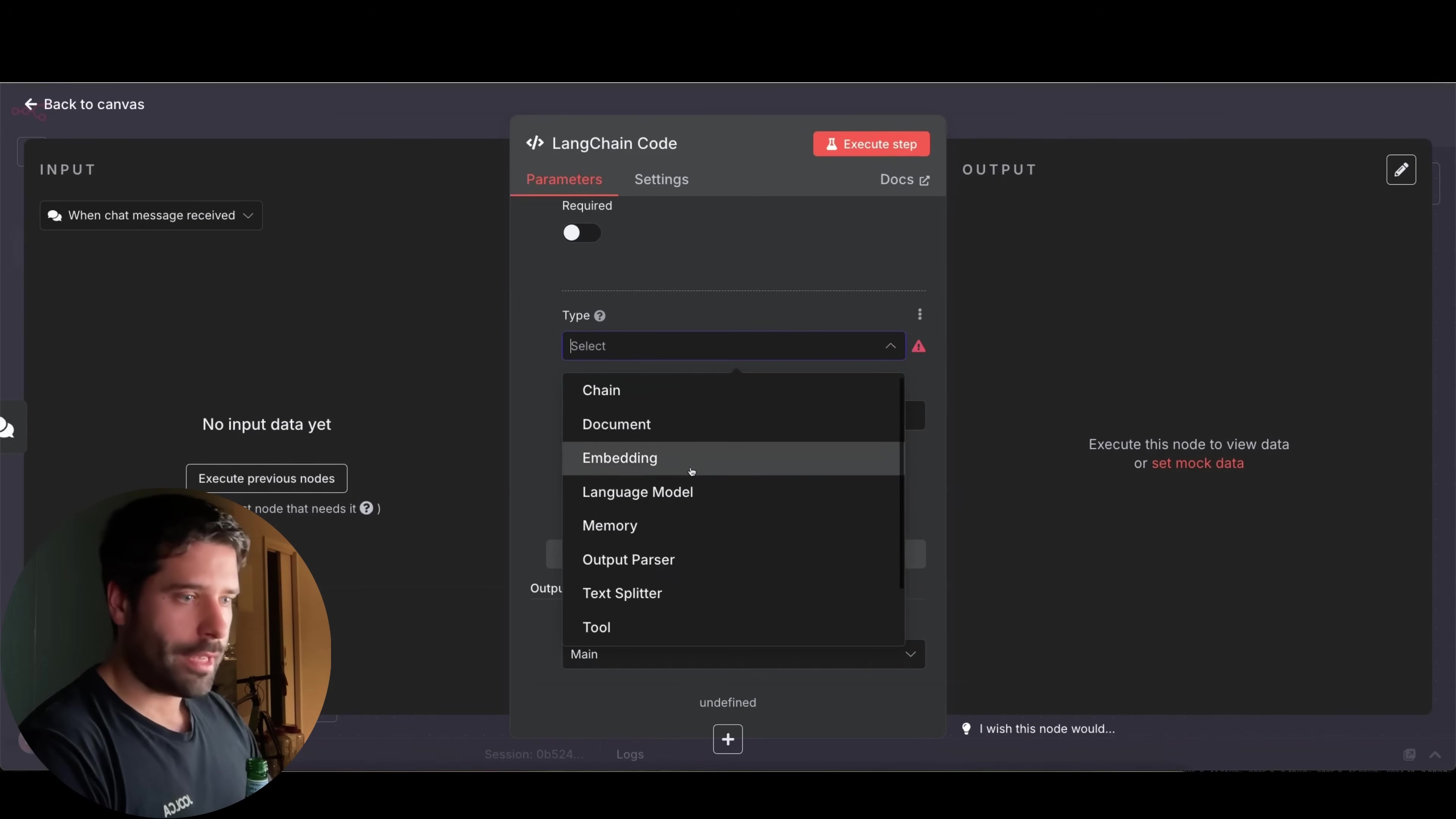
To configure this node, you can add various input and output types, which is where the magic happens. These include:
- ‘Main’: For general input and output, like the main text your agent will process or generate.
- ‘Language Model’: This is crucial! It’s how you connect your AI agent to the actual brain – your chosen Large Language Model (LLM) like OpenAI’s GPT-4o or Anthropic’s Claude.
- ‘Memory’: For managing conversation history. Ever had an AI agent forget what you just said? Memory solves that! It helps the agent remember past interactions, making conversations much more natural and useful.
- ‘Tool’: This is where you integrate external functionalities. Want your AI agent to search the web, send an email, or query a database? Tools are how it does that! We’ll talk more about tools in a bit.
This flexibility is what allows you to construct highly tailored AI agents that can do way more than just answer questions.
What is LangChain?
Before we go further, let’s quickly chat about LangChain. What even is it? In simple terms, LangChain is like a super-powered toolkit for building applications that use LLMs. It’s not an LLM itself, but rather a framework that helps you connect LLMs to other data sources and tools. It simplifies the whole process of creating sophisticated AI agents, making it easier to string together different components.
Many big players, from Replit building coding co-pilots to Klarna developing customer support agents, are using LangChain under the hood. It’s a testament to its robustness and flexibility.
At its core, an AI agent built with LangChain works like this:
- Input: You give it a prompt or a task.
- LLM Processing: The LLM (the brain) gets the input. But here’s the cool part: it also has access to various “tools” (like a web search, a calculator, or even your own custom API) and a set of “instructions” (how it should behave).
- Dynamic Decision-Making: Based on the input, its instructions, and the tools available, the LLM decides what to do next. It might use a tool, ask for more information, or directly generate an answer.
- Output: Finally, it produces an output, which could be an answer, an action (like sending an email), or a combination of both.
This architecture allows for dynamic decision-making and interaction with diverse systems, such as Shopify, Zendesk, or even your own custom APIs. It’s like giving your AI agent a Swiss Army knife and a clear set of goals!
LangChain vs. OpenAI Assistants API: A Comparative Analysis
Okay, so you might be thinking, “Boyce, this sounds a lot like OpenAI’s Assistants API. What’s the difference?” Great question! While both LangChain and OpenAI’s Assistants API help you create AI agents that can interact with external systems, they’re fundamentally different in terms of flexibility and control. Understanding these differences is super important for picking the right tool for your specific project.
Let’s break it down:
| Feature | LangChain Agents (e.g., via n8n) | OpenAI Assistants API |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Highly customizable; mix different LLMs (OpenAI, Claude, etc.) | Less flexible; only works with OpenAI models (ChatGPT, GPT-4o) |
| Tool Integration | Works with external tools (APIs, webhooks, databases) using custom logic | Uses function calling for predefined tools; less customizable |
| How It Works | Framework to help AI think step-by-step and use tools; you define logic | OpenAI handles logic; you send messages, and it decides tool calls |
| Memory & Agents | Build your own agent memory system (n8n, vector DBs) | Built-in memory (stored on OpenAI’s servers) |
| Use Case Fit | Ideal for power users needing control and cross-provider flexibility | Great for plug-and-play within OpenAI’s ecosystem |
| Hosted Where? | Runs on your side (in n8n, your server, etc.) | Fully hosted by OpenAI |
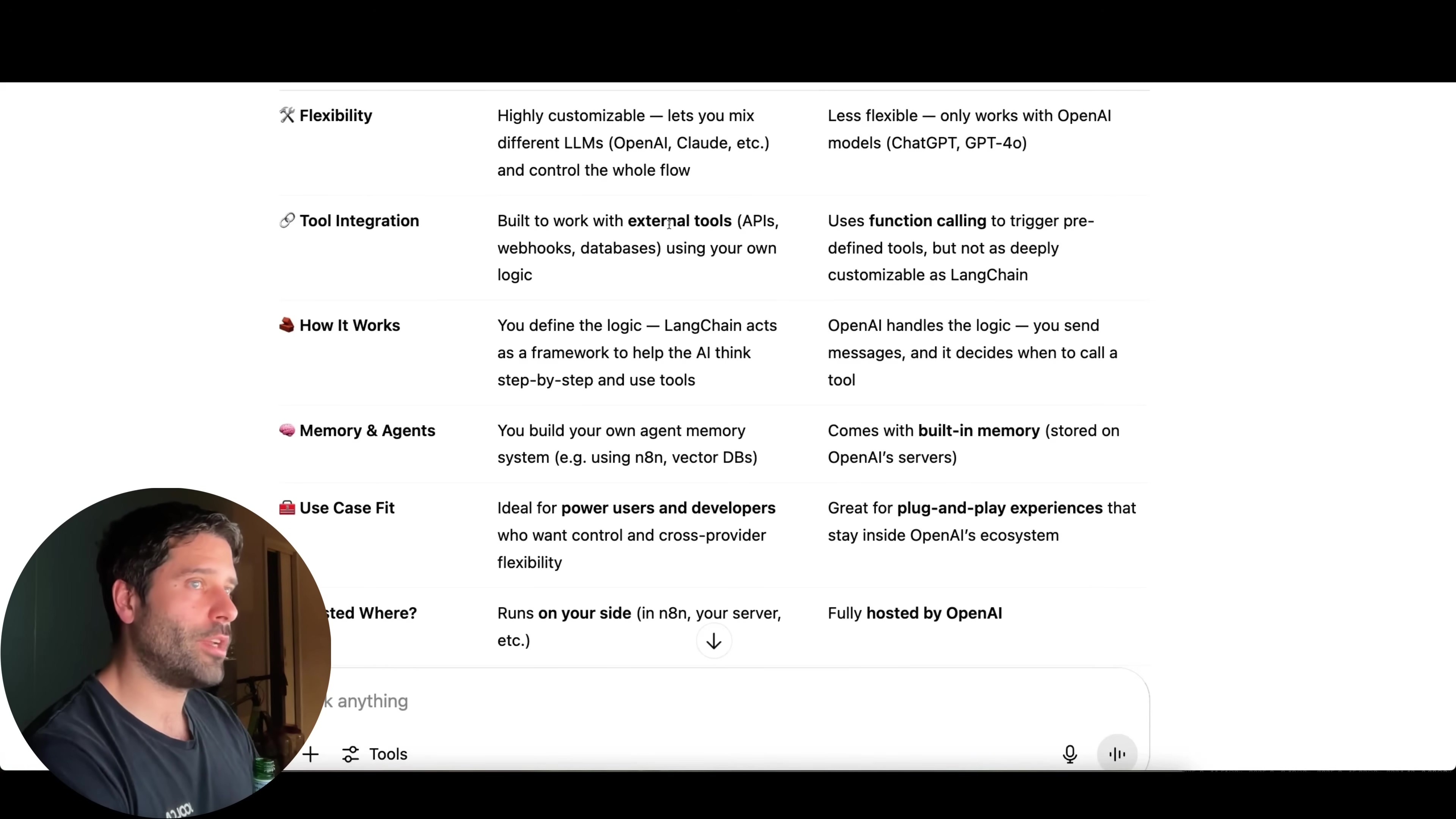
In a nutshell, LangChain empowers you to build your AI agent’s “brain” with full control over which models to use, which tools it can access, and how it interacts with your systems. This makes it incredibly adaptable. The OpenAI Assistants API, while powerful and easy to get started with, operates within OpenAI’s infrastructure and models. It’s more of a “black box” where OpenAI handles a lot of the underlying logic for you. So, if you need ultimate control and the ability to swap out LLMs or integrate with any system, LangChain is your go-to. If you’re happy staying within the OpenAI ecosystem and want something quick and easy, the Assistants API is fantastic.
Advanced Monitoring with LangSmith
Since n8n’s AI agents are built on LangChain, there’s another super handy tool you can leverage: LangSmith, a specialized reporting platform from the same folks who made LangChain. This is where things get really interesting for debugging and optimizing your AI agents.
LangSmith gives you detailed insights into your AI agent’s calls. It’s like having a full diagnostic report for every single thought process your AI agent goes through. You get a comprehensive breakdown of:
- Execution: What steps did it take?
- Token Consumption: How many tokens (the building blocks of LLM communication) did it use? This is crucial for managing costs!
- Failures: Where did it stumble? And why?
- Runtime: How long did each step take?
By integrating LangSmith with your n8n workflows (currently, this is primarily for self-hosted n8n instances, so keep that in mind!), you can literally monitor every single step of an agent’s operation. This includes visualizing the agent’s internal thought process – you can see exactly how it decided to use a tool, what it passed to the LLM, and what the LLM returned. It’s like peeking into the AI’s brain!
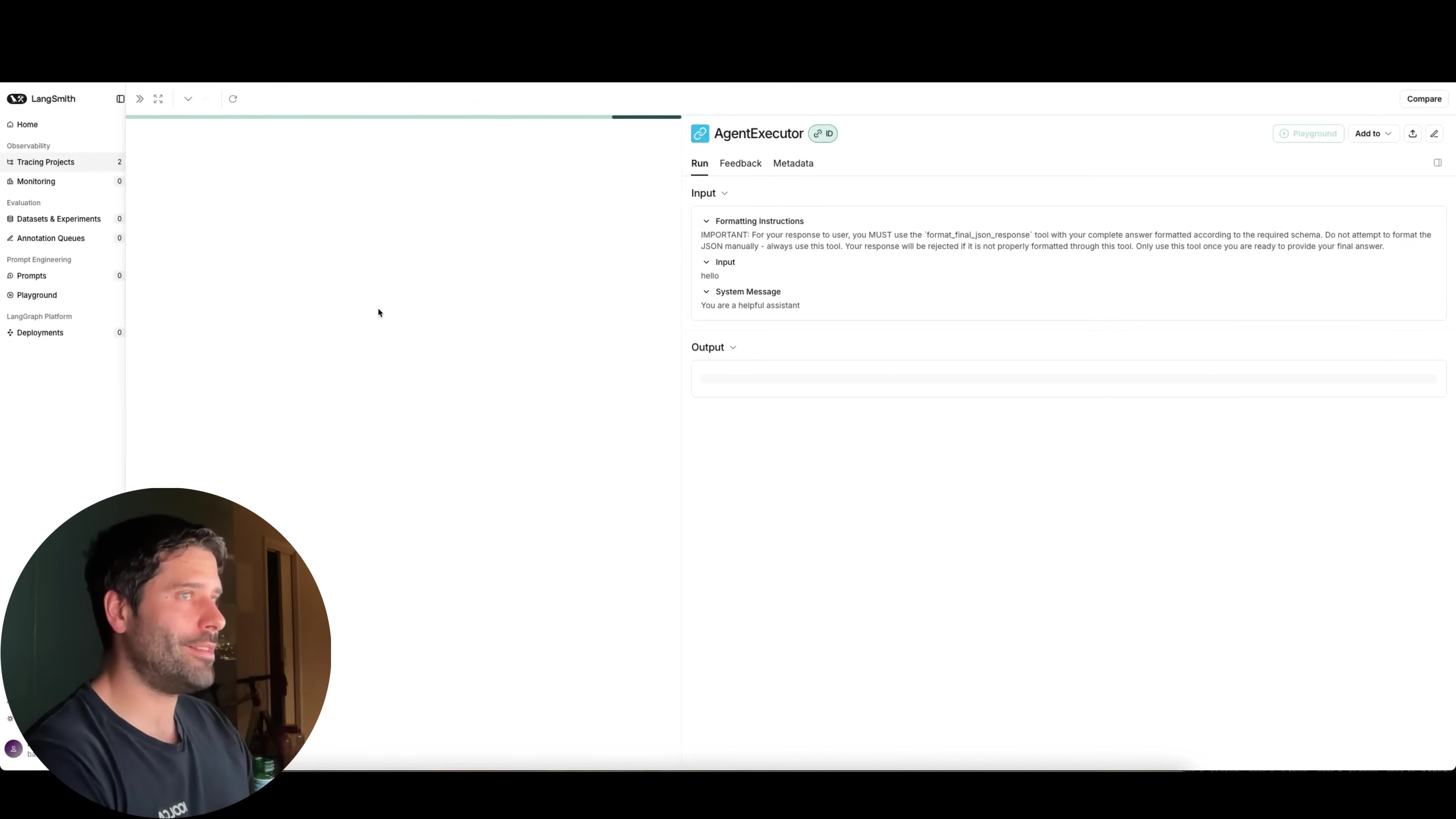
This level of observability is absolutely invaluable. Trust me, when you’re building complex agents, debugging can be a nightmare. LangSmith turns that nightmare into a manageable puzzle. It helps you:
- Debug complex agents: Pinpoint exactly where things went wrong.
- Optimize performance: Identify bottlenecks and areas where your agent is being inefficient.
- Understand AI behavior: Get a deep understanding of how your AI agents are processing information and interacting with tools.
It’s like having X-ray vision for your AI workflows!
Building Customizable AI Agents with LangChain Code Node
Now, for the main event! The true power of the LangChain Code Node lies in its ability to let you write custom JavaScript code. This means you get to define exactly how your AI agent operates. No more being limited by pre-set options! You can build complex workflows, make dynamic decisions, and even orchestrate entire teams of AI agents. It’s like being the conductor of an AI orchestra!
Customizing Agent Actions with Code
Within the LangChain Code Node, you’re basically writing the script for your LLM. You can programmatically define its actions, giving it superpowers like:
- Dynamic Tool Selection: Imagine your agent needing to decide between searching Google, checking an internal database, or sending an email, all based on the user’s query. With code, your agent can intelligently decide which tool to use based on the context. It’s like giving your agent a brain that can pick the right tool for the job, every single time.
- Conditional Logic: This is where you implement
if-elsestatements and loops. For example, “IF the user asks about product availability, THEN check the inventory database. ELSE IF they ask about shipping, THEN use the shipping calculator tool.” This allows you to create sophisticated decision-making processes that adapt to different scenarios. - Multi-Agent Orchestration: This is next-level stuff! You can build teams of agents, each with a specialized role. For instance, one agent could be a “researcher” that gathers information, another a “summarizer” that condenses it, and a third a “responder” that crafts the final answer. You can then manage task handoffs between them, creating a truly collaborative AI system.
- Multiple LLM Integration: Don’t want to be stuck with just one LLM? No problem! You can connect to various LLMs within a single workflow. Maybe you use Anthropic’s Claude for initial request review (because it’s great at summarization), and then switch to OpenAI’s GPT-4 for data processing (because it excels at complex reasoning). The LangChain Code Node makes this seamless.
This level of programmatic control opens up a universe of possibilities for creating highly autonomous and intelligent AI agents that can adapt to changing conditions and perform complex, multi-step tasks. It’s like giving your AI agent the ability to learn and improvise!
LangChain Code Node vs. Pre-built AI Nodes
So, why bother with the LangChain Code Node when n8n has those convenient pre-built AI nodes like the Information Extractor or Text Classifier? Good question! Think of it this way:
- Pre-built AI nodes: These are like ready-made meals. They’re super convenient and get the job done quickly for common tasks. They essentially encapsulate pre-written LangChain code. But because they’re designed for specific functions, they offer limited customization of their underlying logic. You can’t really change the recipe.
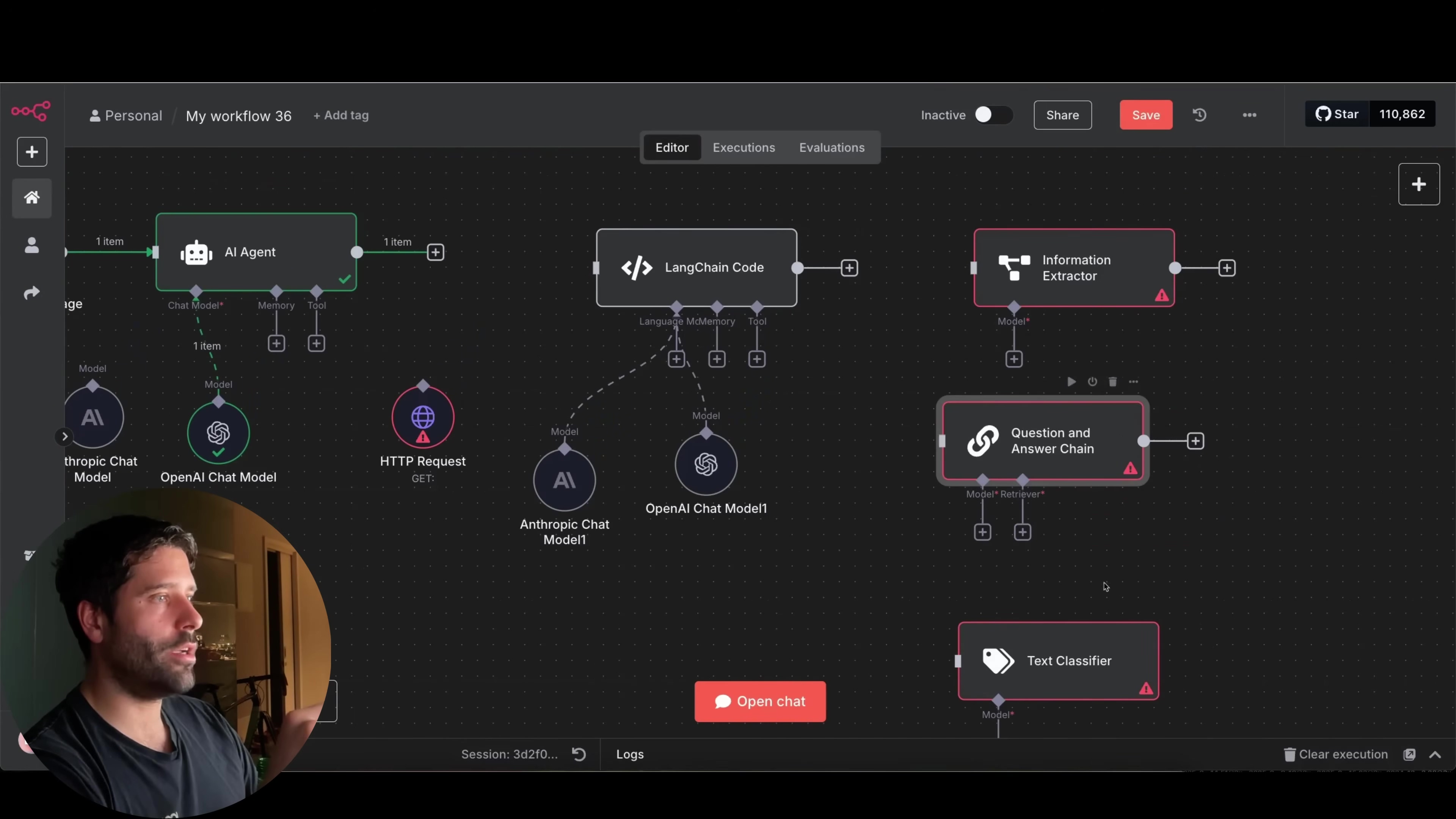
- LangChain Code Node: This is your fully equipped kitchen. You get to define the behavior of your agent from scratch. You can dynamically add inputs and outputs, define custom instructions, and implement complex internal logic. For instance, a Text Classifier built with the LangChain Code Node could have dynamic categories and descriptions. This means you could update your classification rules on the fly, without having to hardcode them. It’s like being the head chef, creating bespoke dishes!
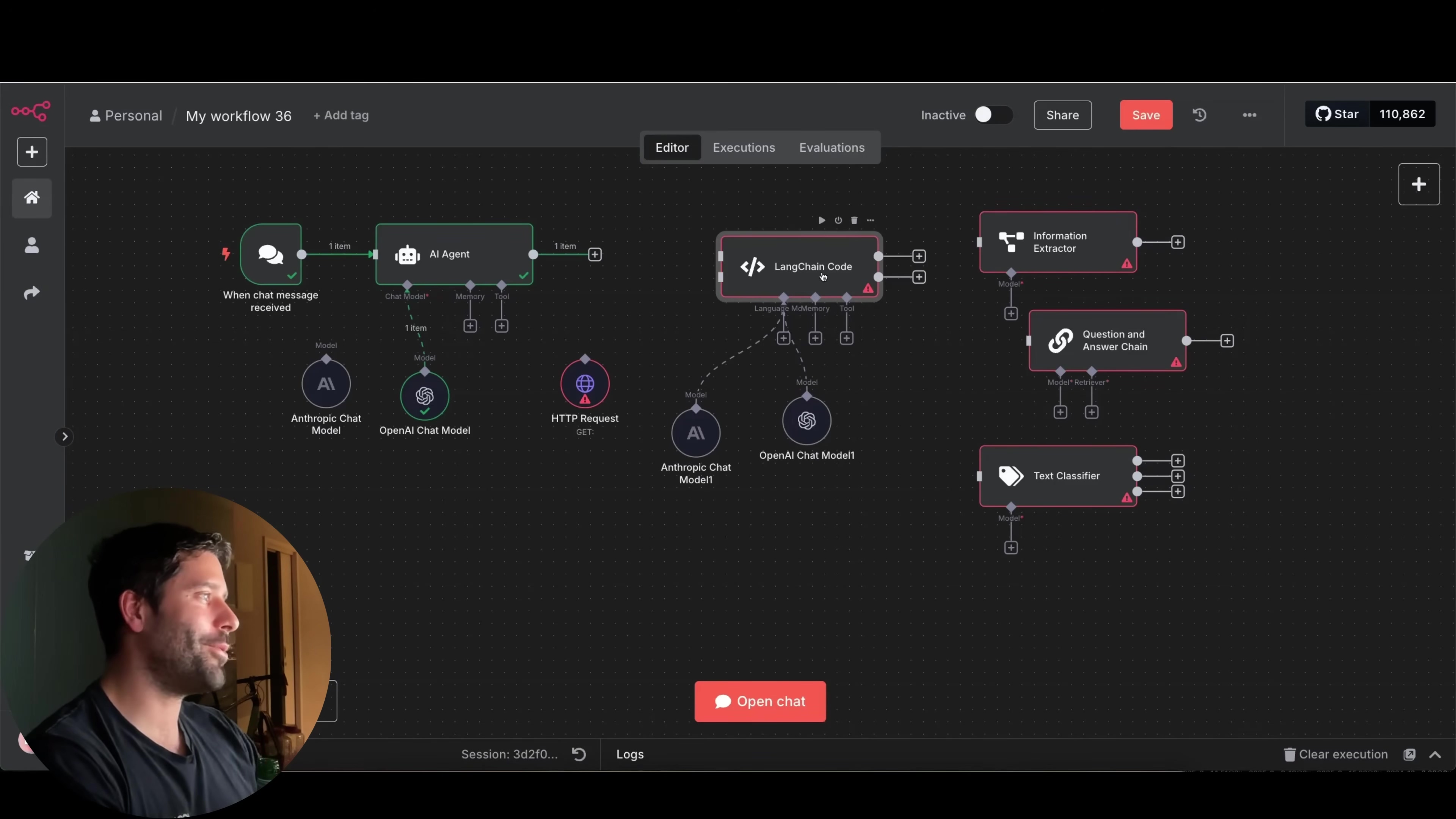
So, while the pre-built nodes are fantastic for quick wins, the LangChain Code Node is for when you need to build something truly unique and powerful. It’s for when you want to go from a ready-made solution to a custom-engineered masterpiece.
Critical Safety / Best Practice Tips
Alright, before you go off building your AI empire, a few words of wisdom from someone who’s learned the hard way:
💡 Input Validation: This is HUGE. Always, always, always validate and sanitize inputs to your AI agents, especially when they’re interacting with external systems. Why? Because you don’t want someone injecting malicious code or causing unexpected behavior. Think of it as putting a bouncer at the door of your AI system – only the good stuff gets in!
💡 Rate Limiting & Cost Management: LLMs are powerful, but they can also be expensive if you’re not careful. Be mindful of API call limits and potential costs associated with LLM usage. Implement rate limiting (limiting how many requests your agent can make in a certain time) and cost monitoring. This prevents unexpected bills that can make your wallet cry. Nobody wants a surprise bill from their AI!
💡 Error Handling & Fallbacks: What happens if a tool fails? What if the LLM returns gibberish? Your AI agent needs a plan B (and C, and D!). Design your AI agents with robust error handling and fallback mechanisms. This means thinking: “If X goes wrong, what should the agent do? Should it try again? Inform the user? Switch to a different tool?” A resilient agent is a happy agent (and a happy user!).
Key Takeaways
So, what have we learned today, my fellow automation enthusiast?
- The LangChain Code Node is the foundational component for many AI agent functionalities in n8n. It’s the secret sauce!
- It offers unparalleled customization, allowing for dynamic inputs, outputs, and complex internal logic. You’re the architect!
- LangChain provides a flexible framework for building AI agents that can integrate with any LLM, tool, or memory component. Freedom to choose!
- LangSmith offers advanced monitoring and reporting for LangChain-based AI agents, providing deep insights into their performance. Your AI’s X-ray vision!
- While more complex to use due to requiring code, the LangChain Code Node unlocks the ability to build highly autonomous and specialized AI agents within n8n. The power is in your hands!
In summary, the LangChain Code Node in n8n offers a powerful pathway to building highly customized and autonomous AI agents. By understanding and leveraging this node, you can move beyond pre-defined functionalities and craft AI solutions that precisely meet your unique needs and integrate seamlessly with diverse systems.
While n8n provides an excellent low-code environment for automation, diving into the LangChain framework via the Code Node offers a deeper level of control, akin to developing in a custom-coded environment. For most common use cases, the standard n8n AI Agent node is sufficient. However, for those requiring intricate, multi-agent orchestrations, dynamic tool interactions, or bespoke LLM integrations that span across providers, the LangChain Code Node is indispensable.
Now, armed with this knowledge, consider exploring the LangChain Code Node in your n8n workflows. I can’t wait to see what amazing, intelligent agents you’ll build! Share your insights and unique agent creations in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why should I use the LangChain Code Node instead of the standard AI Agent node?
A: The standard AI Agent node is fantastic for quick setups and common tasks. But if you need to build highly customized AI agents with specific logic, dynamic tool selection, multi-LLM integration, or complex conditional workflows, the LangChain Code Node gives you the granular control to write custom JavaScript code and define exactly how your agent behaves. It’s like choosing between a pre-built house and designing your dream home from scratch.
Q: Is the LangChain Code Node difficult to use for beginners?
A: Honestly, yes, it’s a bit more advanced than the drag-and-drop nodes in n8n because it requires some JavaScript coding. But don’t let that scare you! If you’re comfortable with basic coding concepts, or even just curious to learn, the power it unlocks is well worth the learning curve. Think of it as leveling up your n8n skills!
Q: Can I use different LLMs (like Claude and GPT) within a single LangChain Code Node workflow?
A: Absolutely! That’s one of the coolest features. The LangChain Code Node allows you to connect to various LLMs. You could, for example, use one LLM for initial text summarization and another for complex reasoning or code generation within the same workflow, optimizing for each LLM’s strengths. It’s like having a team of specialized experts working together.
Q: What are “tools” in the context of LangChain agents, and why are they important?
A: “Tools” are external functionalities that your AI agent can use to interact with the outside world. This could be anything from a web search tool, a calculator, an email sender, or even a custom API that connects to your internal systems (like a database or a CRM). They’re super important because they allow your AI agent to go beyond just generating text and actually perform actions and retrieve real-time information, making it much more useful and dynamic.
Q: How does LangSmith help with my n8n AI agents?
A: LangSmith is a monitoring and debugging platform specifically for LangChain-based applications. Since n8n’s AI agents are built on LangChain, you can use LangSmith to get deep insights into your agent’s operations. It shows you the agent’s thought process, token usage, execution path, and any errors. This is invaluable for understanding why your agent behaved a certain way, debugging issues, and optimizing its performance and cost efficiency. It’s like having a detailed flight recorder for your AI agent.