Watch the Video Tutorial
💡 Pro Tip: After watching the video, continue reading below for detailed step-by-step instructions, code examples, and additional tips that will help you implement this successfully.
Table of Contents
Open Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of AI Browser Agents
- What is an AI Browser Agent?
- Key Components: n8n and Airtop
- Building Your AI Browser Agent: Step-by-Step
- Practical Examples
- Setting Up Your Environment
- Required Resources List and Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Critical Safety / Best Practice Tips
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Do I need to be a programmer to build an AI browser agent with n8n and Airtop?
- Q: What are the main costs associated with running an AI browser agent?
- Q: Can I automate tasks on websites that require two-factor authentication (2FA)?
- Q: What if a website changes its layout? Will my agent break?
- Q: Is it safe to use my real login credentials with Airtop profiles?
- Q: How can I monitor my agent’s activity and troubleshoot issues?
Introduction: The Power of AI Browser Agents
Hey there, future automation wizard! Boyce here. Ever dreamt of having a super-smart robot assistant that can surf the web for you, click buttons, type stuff, and even pull out specific info, all at warp speed? And get this – no manual clicking or typing from you! Well, that’s exactly what an AI browser agent promises. It’s like having your own digital clone, but way faster and never complains about repetitive tasks.
We’re going to combine two seriously cool no-code platforms: n8n (think of it as your workflow command center) and Airtop (that’s our web-browsing powerhouse). Together, they let you build these sophisticated agents that can automate a ton of online chores – from grabbing data off websites (that’s “data scraping” for the tech-savvy folks) to managing your social media, all just by giving them natural language commands. Pretty neat, right?
This guide is your step-by-step blueprint. We’ll break down all the pieces and show you exactly how to build one of these bad boys, complete with some real-world examples. Let’s dive in!
What is an AI Browser Agent?
Alright, let’s get down to brass tacks. What exactly is an AI browser agent? Think of it as an intelligent system that can interact with web browsers programmatically. Now, you might be thinking, “Isn’t that just web scraping?” Not quite! While traditional web scraping scripts are great for pulling specific data, these AI agents are on a whole other level. They can actually understand and execute complex instructions you give them in plain English, totally mimicking how a human would browse. It’s like teaching a robot to use a mouse and keyboard, but without the robot!
Their core superpowers usually include:
- Starting and Ending Browser Sessions: This is like opening and closing a web browser tab, but for your agent. Super important for managing resources.
- Navigation: Simply put, telling the browser to go to a specific website address (URL).
- Interaction: This is where the magic happens – clicking on buttons, links, or typing text into forms. Just like you do!
- Querying: Asking the agent to find and extract specific information from the web page it’s currently looking at.
This level of automation is a game-changer. It opens up a universe of possibilities for streamlining those workflows that used to eat up all your time or needed constant manual babysitting. Say goodbye to mind-numbing copy-pasting!
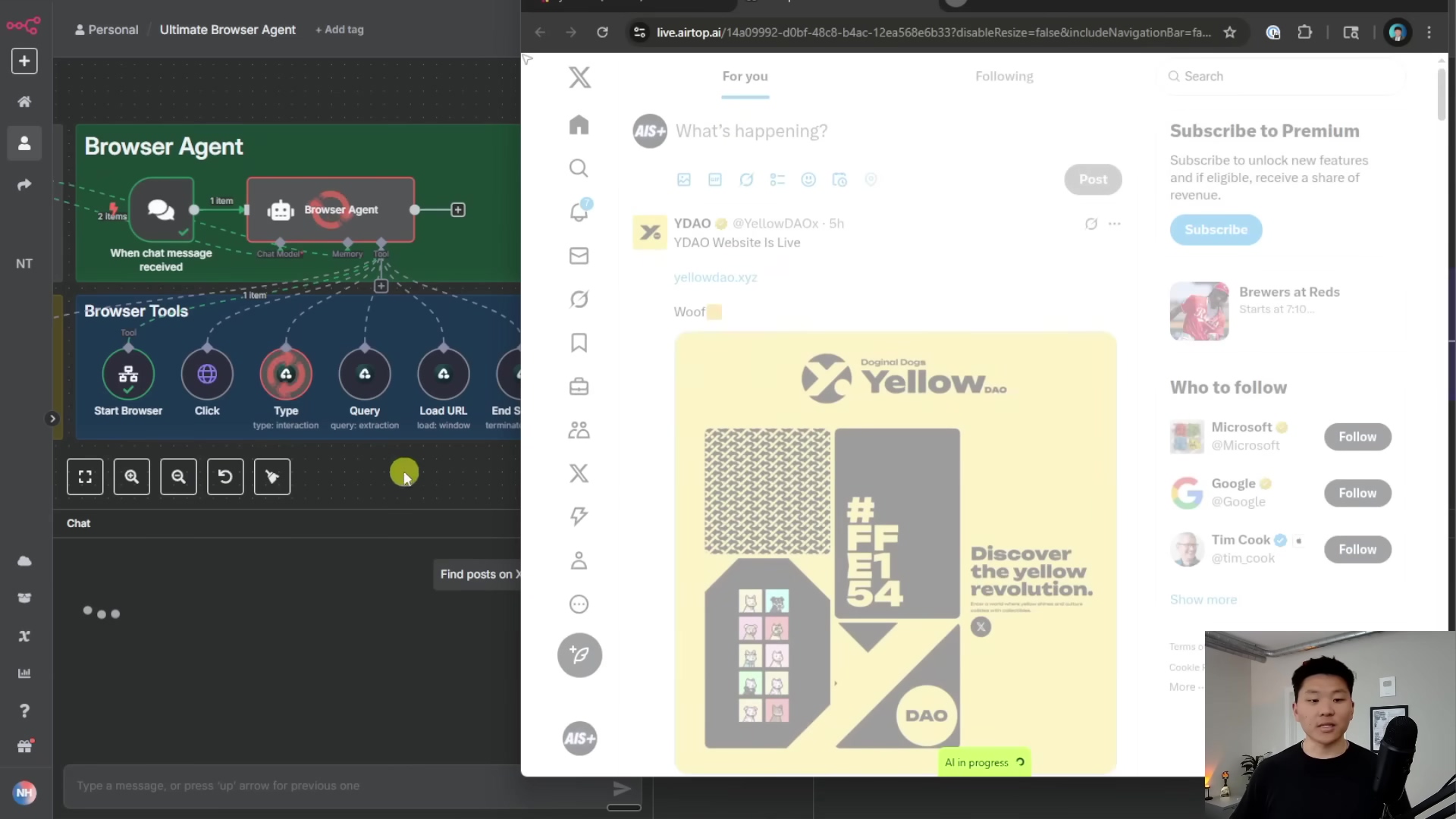
Key Components: n8n and Airtop
Building our AI browser agent is like building a LEGO castle – you need the right bricks! For this project, our two main, super-powered bricks are n8n and Airtop. They work together seamlessly, like a well-oiled machine.
n8n: The Workflow Automation Hub
First up, n8n. If you’ve never heard of it, think of n8n as your central nervous system for automation. It’s an open-source (which means it’s often free to self-host, score!) workflow automation tool that lets you connect pretty much anything – different apps, services, APIs – to automate tasks. It’s like a digital switchboard where you tell different tools how to talk to each other.
In our AI browser agent setup, n8n is the orchestrator. It’s the conductor of our digital orchestra, defining the logic and flow of all our operations. It’s where you’ll build those custom workflows that tell your AI agent when and how to interact with the browser. It’s super visual, so you’ll be dragging and dropping nodes to build your automation masterpiece. If you’re looking for a deep dive, check out their official documentation.
Airtop: The Web Automation Engine
Next, we have Airtop. This is where the real browser magic happens! Airtop specializes in automating web interactions using natural language. It’s the engine under the hood that lets your AI agent actually spin up remote browsers (think of them as virtual web browsers running in the cloud) and perform actions like clicking, typing, and querying. It’s like having a remote-controlled browser farm at your fingertips.
Airtop integrates directly with n8n, which is why they’re such a dynamic duo. This integration is what allows your n8n workflows to execute those complex web tasks we talked about. You can find more about Airtop’s capabilities on their website.
Building Your AI Browser Agent: Step-by-Step
Alright, let’s roll up our sleeves and start building! This is where we turn theory into practice. Don’t worry, I’ll walk you through each step, just like I learned.
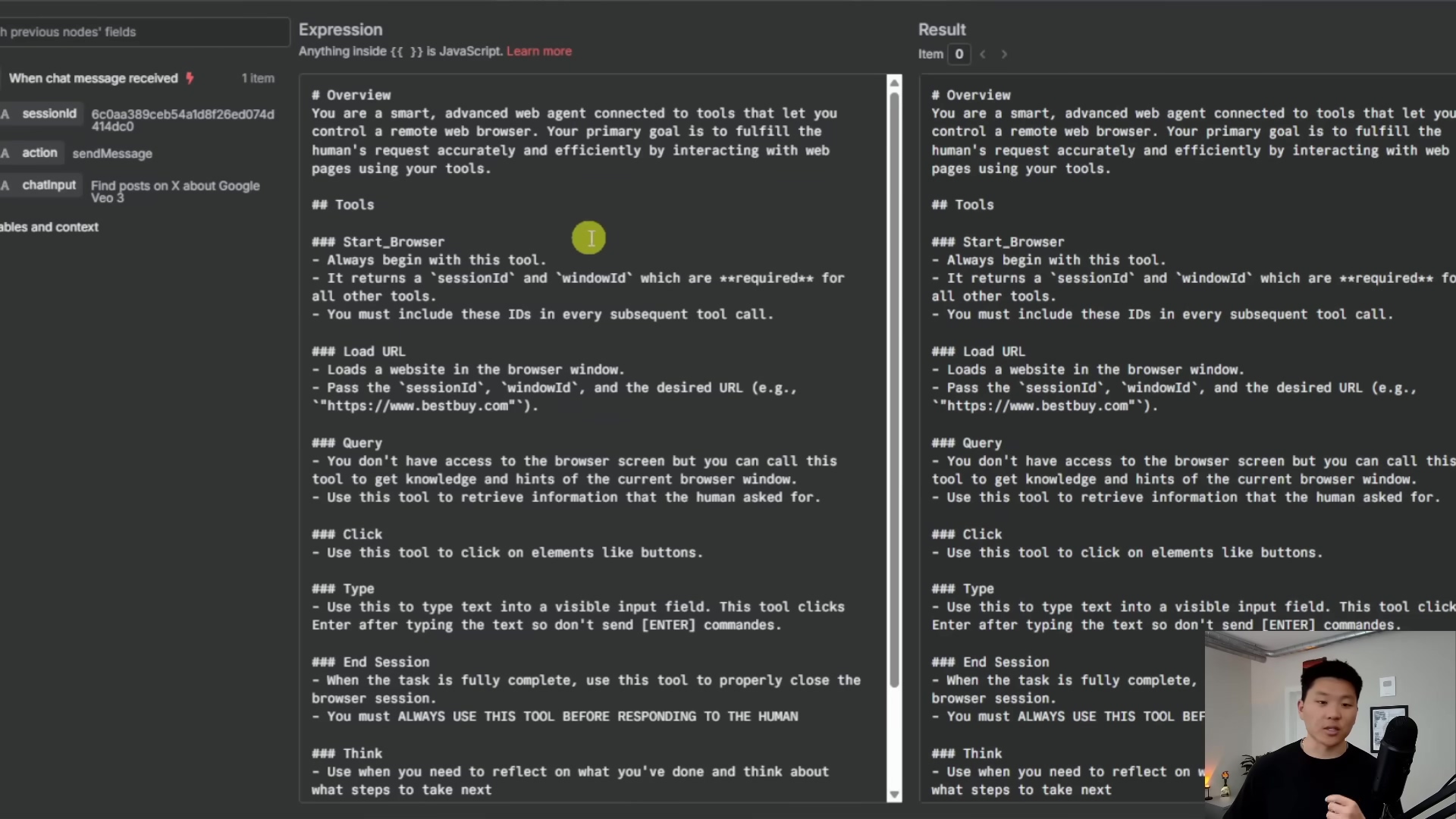
1. Defining the Agent’s Capabilities (System Prompt)
This is arguably the most crucial first step. Imagine you’re giving your AI agent its job description and a list of tools it can use. This is done through something called a system prompt. It’s basically a set of instructions you give to your Large Language Model (LLM) – like Claude 3.5 Sonnet or GPT-4 – that tells it what its primary goal is (e.g., “You are an AI assistant that fulfills human requests by interacting with web browsers”) and, most importantly, what tools it has at its disposal. Think of these tools as special skills your agent can call upon.
Here are the core tools we’ll be giving our agent:
- Start Browser: This is the first thing your agent will do. It kicks off a new browser session, and when it’s done, it gives you back a
sessionIDand awindowID. These are like unique identifiers for that specific browser tab, and you’ll need them for all subsequent actions within that session. Without these IDs, your agent won’t know which browser to interact with! - Load URL: Simple but powerful. This tool tells the browser to go to a specific web address. Useful for direct navigation.
- Query: This is your agent’s “eyes.” It scans the current browser window and extracts information based on a prompt you give it. For example, “Find the price of the first laptop listed.”
- Click: Simulates a mouse click on a specific element on the page. This could be a button, a link, or anything clickable.
- Type: This is your agent’s “keyboard.” It enters text into an input field (like a search bar or a login box) and automatically presses Enter for you. Super handy!
- End Session: Crucial! This tool terminates the browser session. Always, always, always include this at the end of your workflow. Why? Because leaving browser sessions open is like leaving your car running in the driveway – it wastes resources and can rack up unnecessary costs with services like Airtop.
- Think: This is a cool one! It allows the agent to pause, reflect on what it’s done so far, and plan its next steps. It’s especially useful for complex tasks where the agent needs to strategize a bit.
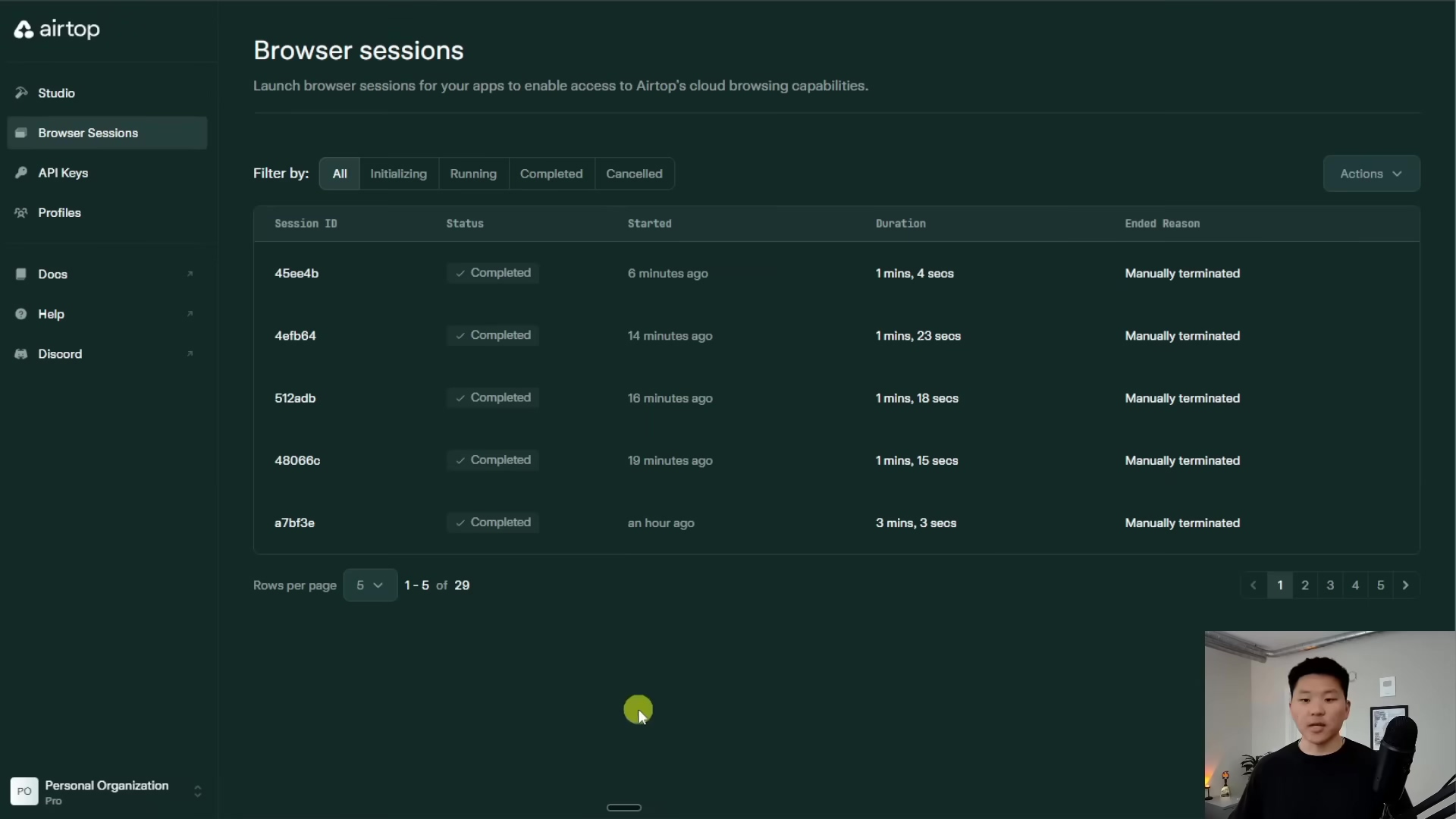
2. Setting Up the ‘Start Browser’ Tool
Okay, let’s get practical. The Start Browser tool isn’t just a concept; it’s a real, custom workflow you’ll build inside n8n. This n8n workflow is specifically designed to talk to Airtop and tell it to launch a remote browser for you. It’s like sending a command to your personal browser-launching service.
When you set this up, you can give it parameters like a target URL (e.g., https://twitter.com/) if you want the browser to open directly to a specific page. You can also include an optional profile name – this is super useful for authenticated sessions, which we’ll talk about later. Think of a profile name as telling Airtop, “Hey, open this browser, but also log me in as ‘Boyce’ using my saved credentials!”
What to expect: When this tool runs successfully, Airtop will spin up a browser, and then it will return two very important pieces of information back to your n8n workflow: a sessionID and a windowID. These IDs are like the unique address of your newly opened browser tab. Every single subsequent action you want your agent to perform in that browser (typing, clicking, querying) will need these IDs. They tell Airtop which browser session to interact with. These IDs are then passed back to your main agent workflow in n8n, ready for the next step.
3. Implementing Core Interaction Tools: Type and Query
Once you’ve got a browser session up and running (thanks to our Start Browser tool!), your agent can finally start doing stuff inside the web page. This is where the Type and Query tools come into play. They’re like the agent’s hands and eyes.
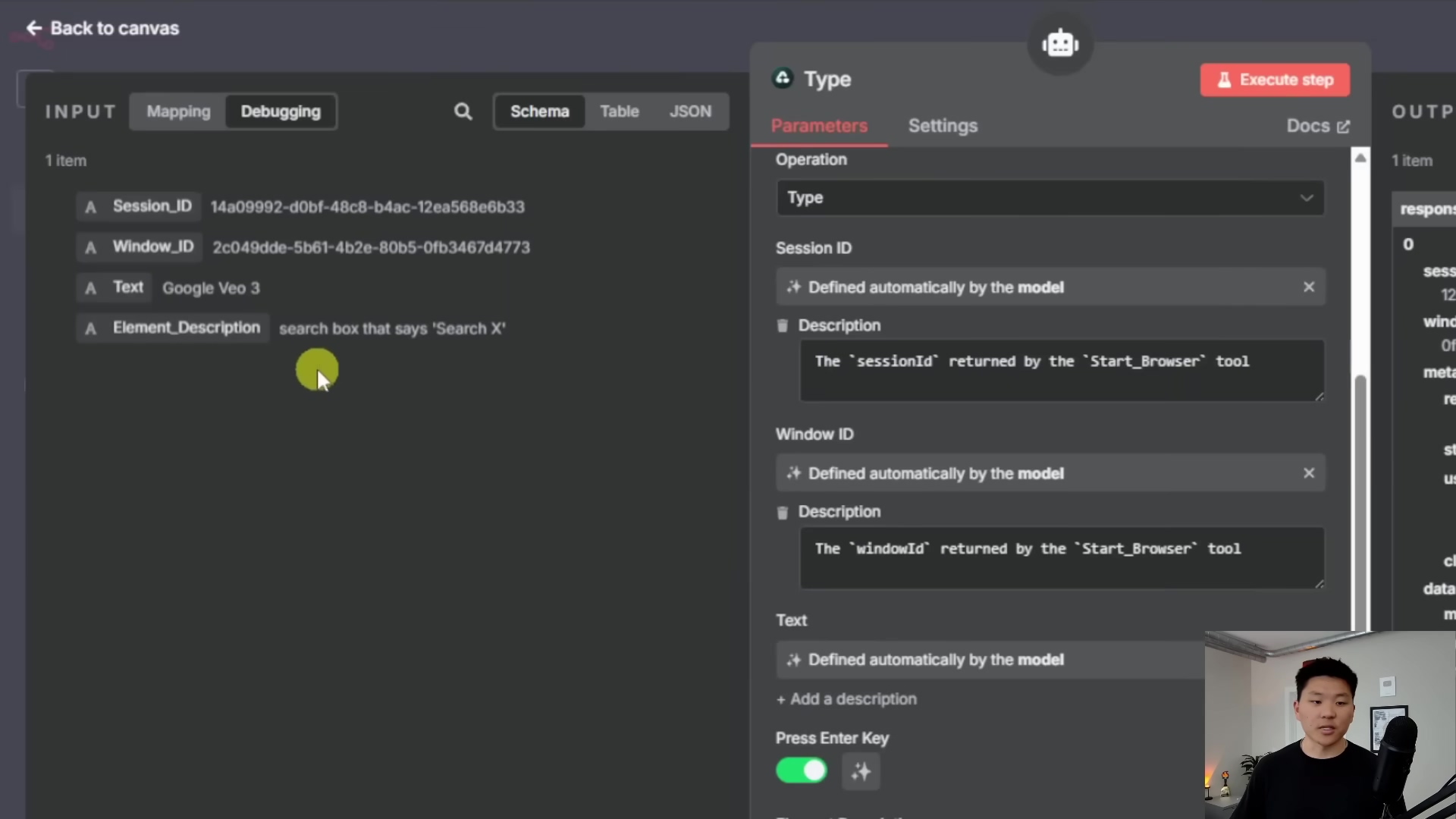
The ‘Type’ Tool
This tool is pretty straightforward. It takes a few key pieces of info:
- The
sessionIDandwindowID(remember those?) - The actual
text to type(e.g., “n8n automation tutorial”) - A
description of the elementyou want to type into. This is where the AI smarts come in! Instead of needing a super technical CSS selector, you can just describe it, like “the search box that says ‘Search X’” or “the input field for email address.” The AI will then figure out where to type.
Your agent uses this to input information into forms, search bars, or any text field. It’s like your agent is physically typing on a keyboard.
The ‘Query’ Tool
This is your agent’s way of reading and understanding the page. The Query tool allows the agent to extract specific information from the current page. You provide it with a prompt (this is where you ask your question!), and it returns the extracted data. For example, you might prompt it with: “What are the search results showing about Google V3? Please summarize the most relevant points and information.” The agent will then process the page content and give you a summarized answer. It’s like asking a smart friend to read a page and tell you the highlights.
4. Handling Dynamic Interactions: Click and Load URL
Websites are dynamic, right? Sometimes you need to click around, and sometimes a direct click might not work as expected. That’s where the Click and Load URL tools become super valuable for more complex scenarios.
The ‘Click’ Tool
This tool is exactly what it sounds like: it simulates a mouse click on buttons, links, or other clickable elements. Just like the Type tool, you’ll provide the sessionID, windowID, and a description of the element to click (e.g., “the ‘Sign In’ button” or “the link that says ‘Read More’”).
Pro-tip: What happens if a direct click fails? Maybe the element isn’t found, or the website’s structure changed. This is where good error handling (which we’ll touch on later) and the Load URL tool come in handy. Your agent can be smart enough to say, “Hmm, I couldn’t click that ‘Products’ link, but I know the products page is usually at www.example.com/products, so I’ll just go there directly!”
The ‘Load URL’ Tool
As mentioned, this tool is used to directly navigate to a specific URL. It’s a fallback or a shortcut. If a click action doesn’t produce the desired result, or if your agent already knows the exact web address it needs to jump to, it can use this tool to get there instantly. It’s like having a bookmark that your agent can instantly jump to.
5. Managing Authenticated Sessions
Ever tried to automate something that requires you to log in? It’s a pain, right? Constantly re-entering usernames and passwords is a non-starter for automation. This is where Airtop’s ‘Profiles’ feature becomes your best friend. It’s invaluable for websites that require you to log in.
Think of ‘Profiles’ as a secure vault within Airtop where you can create and save login credentials for different websites. Once saved, your AI agent can access authenticated content without needing to re-enter those credentials every single time it starts a new session. How cool is that?
How it works: When you use the Start Browser tool, you simply pass the profile name (e.g., “MyTwitterProfile” or “BestBuyLogin”) as a parameter. Airtop then automatically handles the login process for you, spinning up a browser session that’s already authenticated. This is a huge time-saver and makes automating tasks on sites like social media or e-commerce platforms much, much easier.
Practical Examples
Alright, enough talk! Let’s look at some real-world scenarios where our AI browser agent can shine. These examples will help solidify how all those tools come together.
Example 1: Searching X (formerly Twitter)
Imagine you want your AI agent to find all the latest buzz on X (you know, the platform formerly known as Twitter) about a specific topic, like “Google V3.” Here’s how your agent’s workflow might look:
- Start a browser session: Your agent uses the
Start Browsertool. If you want to search within your logged-in account, you’d pass your X profile name here. - Type the search query: It then uses the
Typetool to input “Google V3” into the search bar on X. - Query the page: After the search results load, the agent uses the
Querytool. You’d prompt it with something like, “Summarize the most relevant posts about Google V3, including who posted them and any key dates.” It then extracts and processes that information. - End the session: Crucially, it uses the
End Sessiontool to close the browser and free up resources. - Report the findings: Finally, it sends you the summarized information.
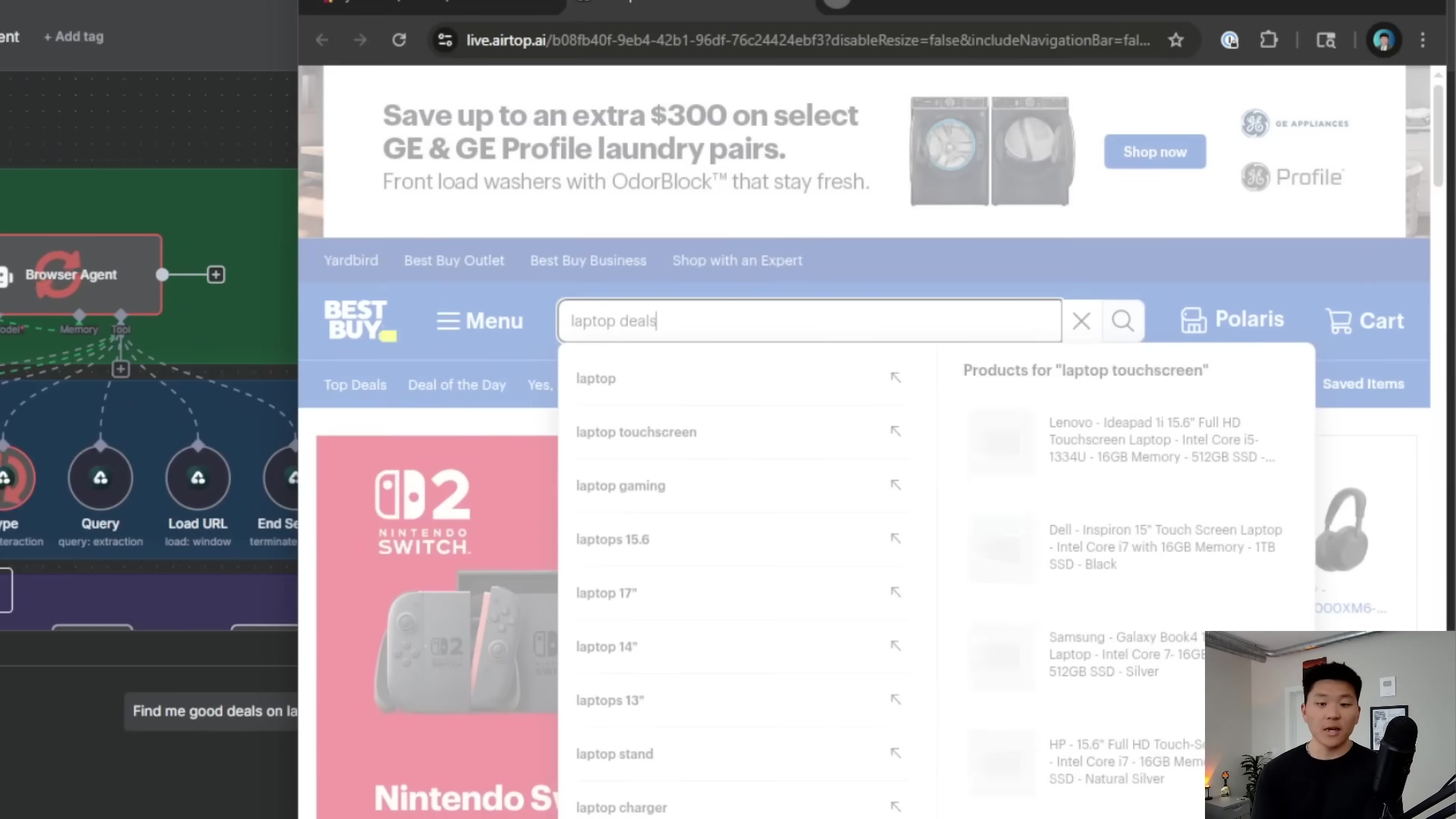
Example 2: Finding Laptop Deals on Best Buy
This is a classic e-commerce automation task. Let’s say you want your agent to find the best laptop deals on Best Buy. Here’s a possible workflow:
- Start a browser session: Again,
Start Browserkicks things off. - Type “laptop deals”: The agent uses the
Typetool to enter “laptop deals” into Best Buy’s search bar. - Attempt to click a link: It then tries to use the
Clicktool to click on a relevant link, perhaps one that says “laptops” or “laptop deals” in the search results. - Fallback to Load URL (if needed): If, for some reason, that click fails (maybe the button moved, or the page changed), the agent is smart enough to use the
Load URLtool to directly navigate to a known deals page, likehttps://www.bestbuy.com/site/laptop/computers(this is where error handling and smart agent design come in!). - Query for deals: Once on the deals page, it uses the
Querytool with a prompt like, “List the top 5 laptop deals, including brand, model, and discounted price.” It then extracts that juicy deal info. - End the session:
End Sessionto clean up. - Summarize the deals: Your agent sends you the list of deals.
Example 3: General Google Search
Even seemingly simple tasks like searching Google for “Yeti water bottle” can be automated, and it’s a great way to test your agent’s basic functionality. Here’s how it would go:
- Start a browser session:
Start Browser– no special profile needed for public searches. - Type “Yeti water bottle”: The agent uses the
Typetool to input the query into the Google search bar. - Query the search results: It then uses the
Querytool to summarize the search results page. You might ask, “What are the top 3 results for ‘Yeti water bottle’ and their descriptions?” - End the session:
End Sessionto wrap things up. - Provide summarized information: The agent delivers the goods.
Setting Up Your Environment
Ready to get your hands dirty? To replicate this awesome setup and build your own AI browser agent, you’ll need a couple of things. Don’t worry, it’s not as complicated as it sounds!
- n8n Instance: You’ll need an n8n instance up and running. You can either self-host n8n (which is free, but requires a bit of technical know-how to set up on your own server or a cloud VM) or use their cloud service. Once you have n8n, you’ll need to connect a chat model to it. This is the brain of your agent! I highly recommend using something like Claude 3.5 Sonnet via OpenRouter (OpenRouter is super cool because it gives you access to a bunch of different LLMs through one API key – very convenient!). This LLM is what gives your agent its intelligence and ability to understand your prompts and decide which tools to use.
- Airtop Account: You’ll also need an Airtop account. Once you sign up, you’ll get an Airtop API key. This key is what allows your n8n instance to securely communicate with Airtop’s web automation engine. Think of it as the secret handshake between n8n and Airtop.
Required Resources List and Cost-Benefit Analysis
Before you jump in, it’s always good to know what resources you’ll need and what the potential costs and benefits are. Transparency is key, right?
Resource List
Here’s a quick rundown of what you’ll need and what it might cost you. Remember, these are estimates, and prices can change!
| Resource/Tool | Description | Estimated Cost (Monthly) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| n8n | Open-source workflow automation platform | Free (Self-hosted) / Paid (Cloud) | If you’re tech-savvy, self-hosting n8n on your own server or a cheap cloud VM (like from DigitalOcean or Vultr) can be free or very low cost. Their cloud plans vary, so check their pricing page. |
| Airtop | Web automation engine for browser interactions | $0 - $380+ (Tiered) | Airtop has a generous free tier that offers 5,000 credits, which is great for getting started and testing! Higher tiers are available if you need more credits or concurrent browser sessions. Check their pricing for details. |
| AI Model | Large Language Model (LLM) for agent intelligence (e.g., Claude, GPT) | Varies by usage | This is usually pay-as-you-go. Costs depend on how many API calls your agent makes and how many “tokens” (think of them as pieces of words) it consumes. Services like OpenAI or Anthropic have their own pricing structures. |
| Slack | (Optional) For receiving live URL notifications and agent responses | Free (Basic) / Paid | This is super useful for real-time monitoring and getting notifications from your agent. You can set up n8n to send messages to Slack channels. The basic Slack plan is free, but paid plans offer more features. |
Cost-Benefit Analysis: DIY AI Agent vs. Commercial Solutions
So, why go through the trouble of building your own AI agent when there are commercial solutions out there? Good question! Let’s break down the pros and cons:
| Feature/Aspect | DIY AI Browser Agent (n8n + Airtop) | Commercial Web Automation Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup Cost | Low (Free tiers available, self-hosting n8n is free) | Moderate to High (Subscription fees, setup costs) |
| Operational Cost | Variable (Based on Airtop credits, LLM API usage) | Predictable (Fixed monthly/annual fees, potential usage overages) |
| Customization | High (Full control over workflows, prompts, and tools) | Limited (Confined by platform’s features and integrations) |
| Scalability | Good (Can scale with n8n and Airtop tiers) | Excellent (Designed for enterprise-level scaling) |
| Learning Curve | Moderate (Requires understanding of n8n, Airtop, and AI prompting) | Low to Moderate (User-friendly interfaces, pre-built templates) |
| Maintenance | Moderate (Requires monitoring workflows, updating tools) | Low (Platform provider handles maintenance and updates) |
| Use Cases | Highly versatile, can be tailored for unique, complex tasks | Best for common, standardized automation needs |
Critical Safety / Best Practice Tips
Alright, before you unleash your AI agent onto the internet, let’s talk about some super important safety and best practice tips. You don’t want to be that person who accidentally crashes a website or racks up a huge bill, right?
⚠️ Always Terminate Sessions: I can’t stress this enough! Make sure your n8n workflows always include the End Session tool to properly close those browser instances. Failing to do so is like leaving your computer on 24/7 – it can lead to resource exhaustion (your server running out of memory) and, more importantly, unnecessary costs from Airtop because those browser sessions are still technically active. Clean up after yourself!
💡 Respect Website Policies: This is a big one for ethical automation. Before you start automating interactions with any website, take a moment to review its terms of service. Look for sections regarding automated access, web scraping, or bot usage. Some sites have very strict policies against browser automation bots, and violating them could lead to your IP address being blocked or even legal trouble. Play nice!
⚠️ Error Handling: The internet is a wild place, and websites change! Elements might move, pages might load slowly, or your internet might hiccup. That’s why implementing robust error handling within your n8n workflows is crucial. This ensures that if a browser interaction fails (e.g., your agent can’t find an element to click), your agent can gracefully recover (maybe try again, or try a different approach) or, at the very least, notify you that something went wrong, rather than just crashing silently. Think of it as giving your agent a “Plan B” and a “Help!” button.
Key Takeaways
So, what have we learned today, my fellow automation enthusiast?
- AI browser agents are a powerful combo of AI smarts and web automation. They let you get tasks done like a human, but with way more efficiency and speed.
- n8n and Airtop are your go-to no-code tools for building and managing these agents. They provide the infrastructure without you needing to write tons of code.
- The brain of your agent is an LLM (like Claude or GPT), guided by a system prompt and a suite of specialized tools for interacting with the web.
- Features like Airtop’s profiles are super handy for dealing with authenticated websites, saving you from constant logins.
- And remember, proper session management (always ending sessions!) and respecting website policies are non-negotiable for effective and ethical automation. Don’t be a digital menace!
Conclusion
Building an AI browser agent with no-code tools like n8n and Airtop is, in my humble opinion, a total game-changer for how we tackle web-based tasks. It’s like having a superpower! By transforming those mind-numbing, complex manual processes into automated, intelligent workflows, these agents offer unparalleled efficiency and scalability. Imagine all the time you’ll save!
While the initial setup does require a bit of a foundational understanding of workflow automation and how to “prompt” an AI, trust me, the long-term benefits in time savings and operational capacity are absolutely substantial. It’s an investment in your future productivity.
Compared to those off-the-shelf commercial solutions, going the DIY route with n8n and Airtop gives you superior customization and control. You can literally tailor the agent precisely to your unique needs, rather than being stuck with what a vendor offers. Of course, it does mean you’ll need to be a bit more hands-on with maintenance and troubleshooting. But for those of us willing to invest a little time in learning, the ability to create highly specialized, autonomous web agents is nothing short of revolutionary. It’s like building your own custom spaceship instead of buying a pre-made one!
Now, you’re armed with the knowledge. Take the leap, my friend, and start building your own AI browser agent to automate your most tedious online tasks. And hey, once you’ve built something cool, share your experiences and creations in the comments below – I’d absolutely love to see what you come up with!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Do I need to be a programmer to build an AI browser agent with n8n and Airtop?
A: Absolutely not! That’s the beauty of “no-code” tools like n8n and Airtop. While a basic understanding of logic and how websites work is helpful, you don’t need to write a single line of code. You’ll be using visual interfaces to drag, drop, and connect different blocks (nodes) to build your workflows. It’s more like building with LEGOs than writing a novel in a foreign language.
Q: What are the main costs associated with running an AI browser agent?
A: The primary costs typically come from two areas: Airtop credits (which you use for browser sessions) and the usage of the Large Language Model (LLM) API (like Claude or GPT). Both are usually pay-as-you-go, meaning you only pay for what you use. Self-hosting n8n can keep that part free, but if you opt for their cloud service, that’s another potential cost. Always keep an eye on your usage dashboards to avoid surprises!
Q: Can I automate tasks on websites that require two-factor authentication (2FA)?
A: Automating 2FA can be tricky and is generally not recommended for security reasons. Airtop’s profiles feature helps with standard username/password logins, but 2FA often requires real-time human interaction (like entering a code from your phone). For tasks requiring 2FA, it’s often best to consider alternative automation methods or manual intervention for that specific step.
Q: What if a website changes its layout? Will my agent break?
A: This is a common challenge in web automation! Yes, if a website significantly changes its layout or the way elements are identified, your agent’s Click or Type tools (which rely on element descriptions) might stop working correctly. This is why robust error handling and regular monitoring of your workflows are important. Sometimes, you’ll need to update your agent’s instructions or element descriptions in n8n to adapt to the new website structure. It’s like giving your robot new glasses when the world changes a bit.
Q: Is it safe to use my real login credentials with Airtop profiles?
A: Airtop is designed with security in mind, and their profiles feature is built to securely store credentials. However, as with any online service, it’s crucial to use strong, unique passwords and enable any available security features. For highly sensitive accounts, always weigh the risks and benefits of automation. If you’re concerned, consider using dedicated accounts for automation tasks where possible.
Q: How can I monitor my agent’s activity and troubleshoot issues?
A: n8n provides execution logs and debugging tools that show you exactly what happened during a workflow run, including any errors. You can also integrate n8n with communication tools like Slack or email to receive real-time notifications about your agent’s progress or any failures. This proactive monitoring is key to quickly identifying and fixing problems.